Kubernetes has skilled great development in its adoption since 2014. Impressed by Google’s inside cluster administration answer, Borg, Kubernetes simplifies deploying and administering your functions. Like all container orchestration software program, Kubernetes is changing into widespread amongst IT professionals as a result of it’s safe and easy. Nevertheless, as with each instrument, recognizing how its structure helps you utilize it extra successfully.
Let’s be taught concerning the foundations of Kubernetes structure, beginning with what it’s, what it does, and why it’s vital.
What’s Kubernetes structure?
Kubernetes or Kubernetes structure is an open-source platform for managing and deploying containers. It offers service discovery, load balancing, regenerative mechanisms, container orchestration, container runtime, and infrastructure orchestration targeted on containers.
Google created the adaptable Kubernetes container administration system, which handles containerized functions throughout many settings. It helps automate containerized software deployment, make modifications, and scale up and down these functions.
Kubernetes is not solely a container orchestrator, although. In the identical method, desktop apps function on MacOS, Home windows, or Linux; it’s the working system for cloud-native functions as a result of it serves because the cloud platform for these applications.
What’s a container?
Containers are a normal method for packaging functions and their dependencies in order that the functions might be executed throughout runtime environments simply. Utilizing containers, you possibly can take important measures towards decreasing deployment time and growing software dependability by packaging an app’s code, dependencies and configurations right into a single, easy-to-use constructing block.
The variety of containers in company functions can develop into unmanageable. To get probably the most out of your containers, Kubernetes helps you orchestrate them.
What’s Kubernetes used for?
Kubernetes is an extremely adaptable and expandable platform for operating container workloads. The Kubernetes platform not solely offers the atmosphere to create cloud-native functions, nevertheless it additionally helps handle and automate their deployments.
It goals to alleviate software operators and builders of the hassle of coordinating underlying compute, community, and storage infrastructure, permitting them to focus solely on container-centric processes for self-service operation. Builders may also create specialised deployment and administration procedures, together with larger ranges of automation for functions made up of a number of containers.
Kubernetes can deal with all vital backend workloads, together with monolithic functions, stateless or stateful applications, microservices, providers, batch jobs, and all the things in between.
Kubernetes is commonly chosen for the next advantages.
- The infrastructure of Kubernetes is superior to that of many DevOps applied sciences.
- Kubernetes breaks down containers into smaller elements for exact administration.
- Kubernetes deploys software program updates swiftly and often.
- Kubernetes offers a platform for creating cloud-native apps.
Kubernetes structure and elements
The essential Kubernetes structure contains many elements, also referred to as K8s elements, so earlier than we soar proper in, it is very important keep in mind the next ideas.
- The essential Kubernetes structure consists of a management airplane that manages nodes and employee nodes that execute containerized apps.
- Whereas the management airplane manages the execution and communication, employee nodes truly run these containers.
- A Kubernetes cluster is a gaggle of nodes, and every cluster has no less than one employee node.
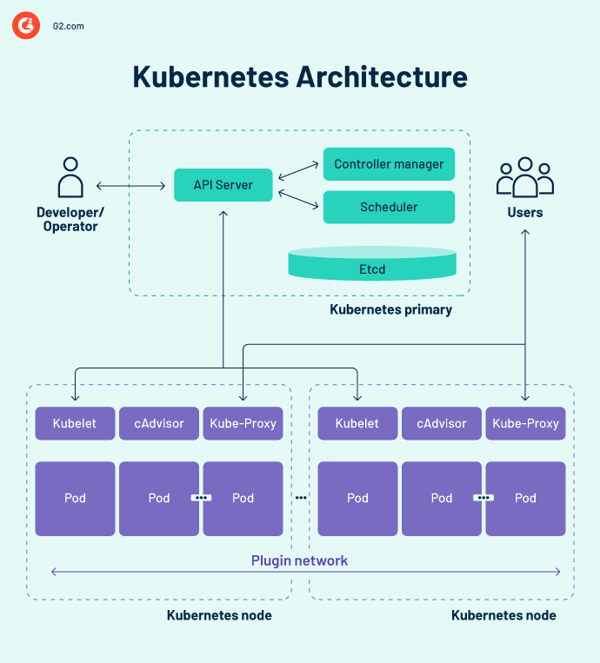
Kubernetes structure diagram
Kubernetes management airplane
The management airplane is the central nervous system heart of the Kubernetes cluster design, housing the cluster’s management elements. It additionally data the configuration and standing of all Kubernetes objects within the cluster.
The Kubernetes management airplane maintains common communication with the compute models to make sure the cluster operates as anticipated. Controllers oversee object states and make system objects’ bodily, noticed state or present standing to suit the specified state or specification in response to cluster modifications.
The management airplane is made up of a number of important parts, together with the software programming interface (API) server, the scheduler, the controller supervisor, and etcd. These elementary Kubernetes elements assure that containers are operating with applicable assets. These elements can all perform on a single main node, however many corporations duplicate them over quite a few nodes for prime availability.
1. Kubernetes API server
The Kubernetes API server is the entrance finish of the Kubernetes management airplane. It facilitates updates, scaling, configures information, and different sorts of lifecycle orchestration by providing API administration for varied functions. As a result of the API server is the gateway, customers should be capable to entry it from outdoors the cluster. On this case, the API server is a tunnel to pods, providers, and nodes. Customers authenticate via the API server.
2. Kubernetes scheduler
The kube-scheduler data useful resource utilization statistics for every computing node, evaluates if a cluster is wholesome, and decides whether or not and the place new containers must be deployed. The scheduler evaluates the cluster’s general well being and the pod’s useful resource calls for, resembling central processing unit (CPU) or reminiscence. Then it chooses an applicable computing node and schedules the duty, pod, or service, contemplating useful resource constraints or assurances, information locality, service high quality necessities, anti-affinity, or affinity requirements.
3. Kubernetes controller supervisor
In a Kubernetes atmosphere, a number of controllers govern the states of endpoints (pods and providers), tokens and repair accounts (namespaces), nodes, and replication (autoscaling). The kube-controller supervisor, typically often known as the cloud controller supervisor or simply the controller, is a daemon that manages the Kubernetes cluster by performing varied controller duties.
The controller displays the objects within the cluster whereas operating the Kubernetes core management loops. It displays them for his or her desired and present states through the API server. If the present and meant states of managed objects don’t match, the controller takes corrective motion to maneuver the thing standing nearer to the specified state. The Kubernetes controller additionally handles important lifecycle duties.
4. etcd
etcd is a distributed, fault-tolerant key-value retailer database that retains configuration information and cluster standing info. Though etcd could also be arrange independently, it typically serves as part of the Kubernetes management airplane.
The raft consensus algorithm is used to maintain the cluster state in etcd. This aids in coping with a typical problem within the context of replicated state machines and requires many servers to agree on values. Raft establishes three roles: chief, candidate, and follower, and creates consensus via voting for a frontrunner.
In consequence, etcd is the only supply of reality (SSOT) for all Kubernetes cluster elements, responding to regulate airplane queries and gathering completely different details about the state of containers, nodes, and pods. etcd can also be used to retailer configuration info like ConfigMaps, subnets, secrets and techniques, and cluster state information.
Kubernetes employee nodes
Employee nodes are methods that run containers the management airplane manages. The kubelet – the core Kubernetes controller – runs on every node as an agent for interacting with the management airplane. As well as, every node runs a container runtime engine, resembling Docker or rkt. Different elements for monitoring, logging, service discovery, and optionally available extras are additionally run on the node.
Some key Kubernetes cluster structure elements are as follows.
Nodes
A Kubernetes cluster should have no less than one computing node, however it may possibly have many extra relying on capability necessities. As a result of pods are coordinated and scheduled to execute on nodes, further nodes are required to extend cluster capability. Nodes do the work of a Kubernetes cluster. They hyperlink functions in addition to networking, computation, and storage assets.
Nodes in information facilities could also be cloud-native digital machines (VMs) or naked steel servers.
Container runtime engine
Every computing node makes use of a container runtime engine to function and handle container life cycles. Kubernetes helps open container initiative-compliant runtimes like Docker, CRI-O, and rkt.
Kubelet service
A kubelet is included on every compute node. It’s an agent that communicates with the management airplane to ensure that the containers in a pod are working. When the management airplane calls for {that a} particular motion be carried out in a node, the kubelet will get the pod specs through the API server and operates. It then makes certain that the associated containers are in good working order.
Kube-proxy service
Every compute node has a community proxy often known as a kube-proxy, which aids Kubernetes networking providers. To handle community connections inside and outdoors the cluster, the kube-proxy both forwards visitors or relies on the working system’s packet filtering layer.
The kube-proxy course of operates on every node to make sure providers can be found to different events and to deal with particular host subnetting. It acts as a community proxy and repair load balancer on its node, dealing with community routing for consumer datagram protocol (UDP) and transmission management protocol (TCP) visitors. The kube-proxy, in actuality, routes visitors for all service endpoints.
Pods
To this point, we have lined inside and infrastructure-related concepts. Pods, nonetheless, are essential to Kubernetes since they’re the first outward-facing part builders work together with.
A pod is the only unit within the Kubernetes container mannequin, representing a single occasion of an software. Every pod contains a container or a number of tightly associated containers that logically match collectively and perform the foundations that govern the perform of the container.
Pods have a finite lifespan and finally die after being upgraded or scaled again down. Though ephemeral, they execute stateful functions by connecting to persistent storage.
Pods can also scale horizontally, which implies they will enhance or lower the variety of situations working. They’re additionally able to doing rolling updates and canary deployments.
Pods function on nodes collectively, so that they share content material and storage and will talk with different pods via localhost. Containers might span a number of computer systems, and so can pods. A single node can function a number of pods, every gathering quite a few containers.
The pod is the central administration unit within the Kubernetes ecosystem, serving as a logical border for containers that share assets and context. The pod grouping methodology, which lets a number of dependent processes function concurrently, mitigates the variations between virtualization and containerization.
Sorts of pods
A number of types of pods play an important function within the Kubernetes container mannequin.
- The default sort, ReplicaSet, ensures that the given variety of pods is operational.
- Deployment is a declarative methodology of managing ReplicaSets-based pods. This consists of rollback and rolling replace mechanisms.
- Daemonset ensures that every node runs an occasion of a pod. Cluster providers resembling well being monitoring and log forwarding are used.
- StatefulSet is designed to handle pods that should endure or protect the state.
- Job and CronJob run one-time or predefined scheduled jobs.
Different Kubernetes structure elements
Kubernetes maintains an software’s containers however can also handle the related software information in a cluster. Customers of Kubernetes can request storage assets with out understanding the underlying storage infrastructure.
A Kubernetes quantity is a listing the place a pod can entry and retailer information. The amount sort determines the amount’s contents, the way it got here to be, and the media that helps it. Persistent volumes (PVs) are cluster-specific storage assets typically supplied by an administrator. PVs may also outlive a given pod.
Kubernetes relies on container photographs, that are saved in a container registry. It is likely to be a third-party register or one which the group creates.
Namespaces are digital clusters that exist inside a bodily cluster. They’re designed to create unbiased work environments for quite a few customers and groups. Additionally they preserve groups from interfering with each other by limiting the Kubernetes objects they will entry. Kubernetes containers inside a pod can talk with different pods via localhost and share IP addresses and community namespaces.
Kubernetes vs. Docker Swarm
Each Kubernetes and Docker are platforms that present container administration and software scaling. Kubernetes offers an efficient container administration answer excellent for high-demand functions with a sophisticated setup. In distinction, Docker Swarm is constructed for simplicity, making it a wonderful alternative for important apps which might be fast to deploy and keep.
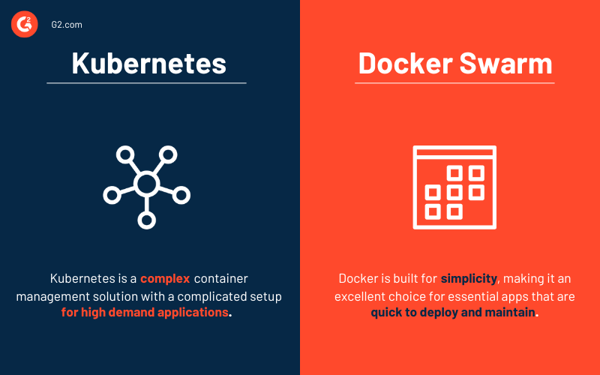
- Docker Swarm is less complicated to deploy and configure than Kubernetes.
- Kubernetes offers all-in-one scalability based mostly on visitors, whereas Docker Swarm prioritizes fast scaling.
- Computerized load balancing is out there in Docker Swarm however not in Kubernetes. Nevertheless, third-party options might hyperlink an exterior load balancer to Kubernetes.
The calls for of your organization decide the appropriate instrument.
Container orchestration options
Container orchestration methods allow builders to launch a number of containers for software deployment. IT managers can use these platforms to automate administering situations, sourcing hosts, and connecting containers.
The next are a number of the greatest container orchestration instruments that facilitate deployment, determine failed container implementations, and handle software configurations.
High 5 container orchestration software program:
*The 5 main container orchestration options from G2’s Spring 2023 Grid® Report.
Kubernetes structure greatest practices and design rules
Implementing a platform technique that considers safety, governance, monitoring, storage, networking, container lifecycle administration, and orchestration is important. Nevertheless, Kubernetes is extensively difficult to undertake and scale, particularly for companies that handle each on-premises and public cloud infrastructure. To simplify it, mentioned beneath are some greatest practices that have to be thought-about whereas architecting kubernetes clusters.
- Be certain that you at all times have probably the most current model of Kubernetes.
- Put money into coaching for the event and operational groups.
- Set up company-wide governance. Be certain that your instruments and suppliers are appropriate with Kubernetes orchestration.
- Improve safety by together with image-scanning strategies in your steady integration and supply (CI/CD) workflow. Open-source code downloaded from a GitHub repository ought to at all times be handled with warning.
- Implement role-based entry management (RBAC) all through the cluster. Fashions based mostly on least privilege and 0 belief must be the norm.
- Solely make the most of non-root customers and make the file system read-only to guard containers additional.
- Keep away from default values since easy declarations are much less vulnerable to errors and higher talk objective.
- When using fundamental Docker Hub photographs, be cautious as a result of they could embrace malware or be bloated with unneeded code. Start with lean, clear code and work your method up. Smaller photos develop extra rapidly, take up much less house on storage, and pull photographs sooner.
- Maintain containers as easy as doable. One course of per container permits the orchestrator to report whether or not or not that course of is wholesome.
- Crash when doubtful. Don’t restart on failure since Kubernetes will restart a failing container.
- Be descriptive. Descriptive labels profit current and future builders.
- In the case of microservices, do not be too particular. Each perform inside a logical code part should not be its microservice.
- The place doable, automate. You possibly can skip handbook Kubernetes deployments altogether by automating your CI/CD workflow.
- Use the liveliness and readiness probes to help in managing pod lifecycles; in any other case, pods could also be terminated whereas initializing or receiving consumer requests earlier than they’re prepared.
Think about your containers
Kubernetes, the container-centric administration software program, has develop into the de facto customary for deploying and working containerized functions because of the broad utilization of containers inside companies. Kubernetes structure is easy and intuitive. Whereas it offers IT managers better management over their infrastructure and software efficiency, there’s a lot to be taught to benefit from the know-how.
Intrigued to discover the topic extra? Study concerning the rising relevance of containerization in cloud computing!


