Physicists have carried out the primary quantum calculations to be carried out utilizing particular person atoms sitting on a floor.
The method, described on 5 October in Science1, controls titanium atoms by beaming microwave alerts from the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM). It’s unlikely to compete any time quickly with the main approaches to quantum computing, together with these adopted by Google and IBM, in addition to by many start-up corporations. However the tactic could possibly be used to check quantum properties in a wide range of different chemical parts and even molecules, say the researchers who developed it.
At some degree, every part in nature is quantum and may, in precept, carry out quantum computations. The arduous half is to isolate quantum states referred to as qubits — the quantum equal of the reminiscence bits in a classical pc — from environmental disturbances, and to regulate them finely sufficient for such calculations to be achieved.
Andreas Heinrich on the Institute for Primary Science in Seoul and his collaborators labored with nature’s ‘authentic’ qubit — the spin of the electron. Electrons act like tiny compass needles, and measuring the course of their spin can yield solely two doable values, ‘up’ or ‘down’, which correspond to the ‘0’ and ‘1’ of a classical bit. However earlier than it’s measured, electron spin can exist in a continuum of doable intermediate states, referred to as superpositions. That is the important thing to performing quantum computations.
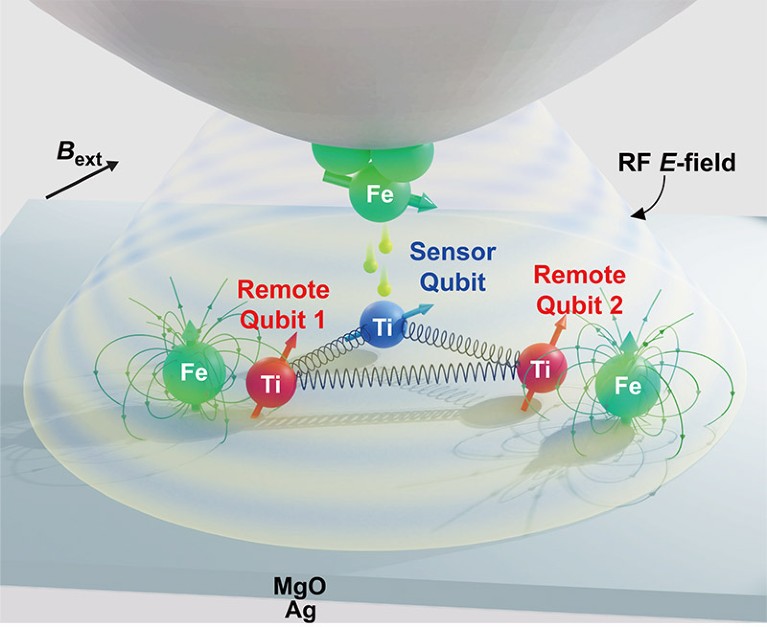
Three titanium atoms are organized inside a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM), shut sufficient to sense one another’s quantum spins. Iron atoms caught to the tip of the STM (high) ‘discuss’ with one of many qubits (blue), utilizing it to learn and write info on the opposite two (crimson) and to get them to carry out a rudimentary quantum computation.Credit score: Heart for Quantum Nanoscience
The researchers began by scattering titanium atoms on a superbly flat floor made from magnesium oxide. They then mapped the atoms’ positions utilizing the STM, which has atomic decision. They used the tip of the STM probe to maneuver the titanium atoms round, arranging three of them right into a triangle.
Utilizing microwave alerts emitted from the STM tip, the researchers have been in a position to management the spin of a single electron in one of many titanium atoms. By tuning the frequencies of the microwaves appropriately, they might additionally make its spin work together with the spins within the different two titanium atoms, equally to how a number of compass needles can affect one another via their magnetic fields. By doing this, the crew was in a position to arrange a easy two-qubit quantum operation, and in addition to learn out its outcomes. The operation took simply nanoseconds — quicker than is feasible with most different forms of qubit.
Heinrich says that will probably be pretty simple to increase the method to maybe 100 qubits, probably by manipulating spins in a mixture of particular person atoms and molecules. It may be troublesome to push it a lot past that, nonetheless — and the main qubit applied sciences are already being scaled as much as lots of of qubits. “We’re extra on the basic-science aspect,” Heinrich says, though he provides that a number of STM quantum computer systems may sooner or later be linked to type an even bigger one.

