The antibiotic drug candidate zosurabalpin killed a number of resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii (pictured) in tradition and one totally resistant pressure in mice.Credit score: George Mattei/SPL
The bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii is a portrait of resilience. The microorganism causes a spread of infections, and its capability to outlive desiccation means it may possibly persist for weeks on hospital air vents, laptop keyboards and human pores and skin. Its metabolic and genetic flexibility have allowed it to change into proof against the few antibiotics that may make it by way of its two protecting cell membranes. Antibiotic-resistant microbes kill multiple million folks annually. The worldwide menace posed by A. baumannii has put the microbe excessive on the checklist of precedence pathogens drawn up by the World Well being Group (WHO).
Two research printed on 3 January in Nature report a brand new class of drug candidates for tackling A. baumannii infections (C. Zampaloni et al. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06873-0 (2023); Okay. P. Pahil et al. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06799-7; 2023). One among these compounds has already made it into scientific trials, however it’s nonetheless a great distance from being authorized for scientific use.
A brand new kind of antibiotic targets a drug-resistant bacterium
The obstacles for creating such compounds aren’t simply scientific: the financial incentives are inadequate for a lot of corporations to take the danger. As the specter of resistance grows, the worldwide group should do extra to shepherd promising medication from bench to bedside.
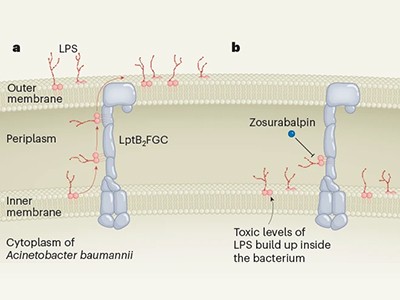
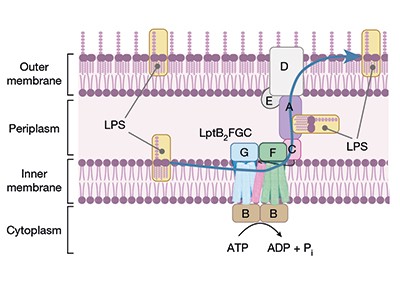
The brand new compounds block the bacterium’s capability to shuttle key constructing blocks to the place they’re wanted, and accomplish that by binding to a novel web site within the bacterium — there are different compounds that focus on this pathway, however A. baumannii is proof against them. One of many molecules, referred to as zosurabalpin, killed a number of resistant strains of A. baumannii in tradition, and, in mice, a pressure proof against all accessible antimicrobials. The primary clinical-trial outcomes for the compound are anticipated this yr.
It’s uncommon to get antibiotics with a brand new mode of motion into the clinic — just one in 30 candidates makes it so far as testing in folks. Even when a brand new drug does get by way of scientific trials and is authorized to be used, it’s typically held in reserve for worst-case eventualities, for concern that widespread use would hasten the day when microbes develop resistance to it.
Clearing the preliminary part of scientific trials shall be solely the start. Additional research will then be wanted to evaluate the danger of resistance to zosurabalpin rising in scientific settings. Then, if the drug is authorized, somebody might want to pay for it. The industrial market is dismal by design. A brand new antibiotic typically prices greater than US$1 billion to develop, however the reluctance to make use of it extensively signifies that it’s more likely to earn lower than $100 million a yr as soon as available on the market. The WHO and others have warned governments concerning the scale of the expense, coupled with the rising menace of antimicrobial resistance. Some governments have responded with incentives to encourage business to take up the problem. However there was way more discuss than motion.
Learn the paper: A novel antibiotic class focusing on the lipopolysaccharide transporter
The answer, well being economists say, is a mixture of incentives for brand spanking new antimicrobial drug improvement. ‘Push’ methods are designed to scale back the prices and might embody extra authorities funding for early-stage analysis. ‘Pull’ approaches reward corporations for creating profitable antibiotics — for instance, governments may assure a minimal degree of buy, much like the superior purchases made from vaccines in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Governments have tended to lean extra in direction of push methods. Economists say they should do extra pulling. However they need to additionally heed classes learnt from COVID-19 vaccines, similar to making certain that pricing and contracts are clear, which didn’t occur in the course of the pandemic.
The UK has been a frontrunner on this regard. In 2019, it launched a ‘subscription’ programme by way of which corporations are paid a hard and fast annual charge that’s based mostly on a drug’s worth to the health-care system, moderately than on the variety of doses offered. Different nations are contemplating related plans. In the US, a bipartisan workforce of lawmakers is backing the Pioneering Antimicrobial Subscriptions to Finish Upsurging Resistance (PASTEUR) Act, which might create the same programme. However the act has struggled within the US Congress because it was first launched in 2020. The European Union has additionally been unable to cross related laws. It’s time for governments to maneuver from consideration to motion.
Some hesitation is comprehensible: the subscription mannequin would put additional strain on health-care budgets which can be already feeling the pressure of drug costs fuelled by excessive ranges of inflation. However there’s one other means to have a look at such funds: as insurance coverage in opposition to future health-care crises. If governments could make the marketplace for these medication viable, that can even encourage corporations to take a position.
In September, the United Nations Normal Meeting will host a high-level assembly to debate antimicrobial resistance — the primary such assembly since 2016. This may spotlight the issue and provide a possibility to extract actual commitments from member states. The final assembly was transformational in a single respect: greater than 150 nations agreed to attract up motion plans to handle antimicrobial resistance.
However an motion plan is just not the identical as taking motion — many plans are neither totally applied nor totally funded. That should change. The invention of compounds that present promising preclinical exercise is exactly what the physician ordered. However with no strategic funding plan, this prescription could possibly be sitting on the shelf for years. All of the whereas, A. baumannii and its ilk will proceed to pose an pressing health-care menace with restricted remedy choices.