In drone survey missions, the selection between photogrammetry and LIDAR relies upon closely on the precise software. You additionally want to contemplate operational components, similar to value and complexity. Understanding what outputs you really want will provide help to make the appropriate determination.
What’s LIDAR and the way does its output evaluate with outcomes obtained with high-resolution RGB cameras and photogrammetry? On this article, we’ll discover the methods photogrammetry and LIDAR are literally fairly completely different from one another, even when their three-dimensional (3D) outputs look related. We’ll then dig deeper into particular functions and the way photogrammetry can present distinctive outcomes for many missions at a fraction of the associated fee and complexity of LIDAR.
Photogrammetry {and professional}, high-resolution cameras can cost-effectively generate 2D and 3D surveys, with absolute accuracies all the way down to 1 cm (0.4 in) root imply sq. (RMS) horizontal and three cm (1.6 in) RMS vertical.
How Photogrammetry Works
In photogrammetry, a drone captures a lot of high-resolution pictures over an space. These photographs overlap such that the identical level on the bottom is seen in a number of pictures and from completely different vantage factors. In an analogous manner that the human mind makes use of data from each eyes to offer depth notion, photogrammetry makes use of these a number of vantage factors in photographs to generate a 3D map.
The outcome: a high-resolution 3D reconstruction that comprises not solely elevation/peak data, but in addition texture, form, and shade for each level on the map, enabling simpler interpretation of the ensuing 3D level cloud.
Drone methods that use photogrammetry are value efficient and supply excellent flexibility when it comes to the place, when, and the way you seize 2D and 3D information.
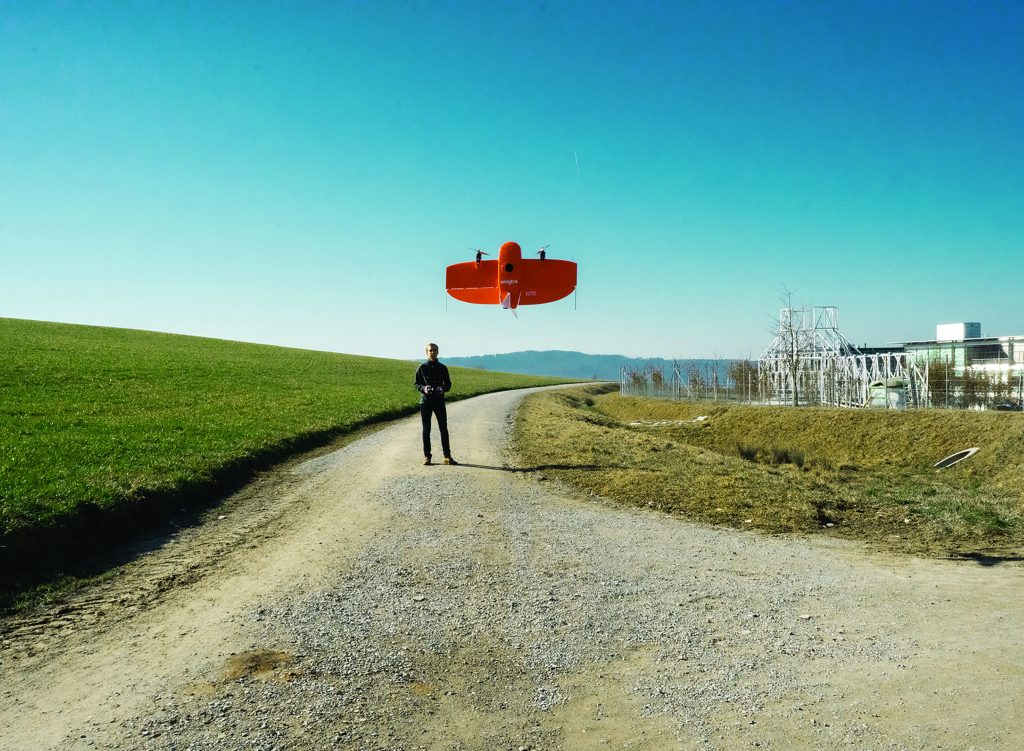

The WingtraOne vertical take-off and touchdown (VTOL) drone permits customers to conduct small- and large-scale drone surveys with unmatched information high quality at a fraction of the time and value of a crewed plane.
HOW LIDAR WORKS
LIDAR, which stands for “mild detection and ranging,” is a expertise that has been round for a lot of many years however has solely not too long ago been obtainable in a dimension and energy possible for carrying on massive drones. A LIDAR sensor sends out pulses of laser mild and measures the precise time it takes for these pulses to return as they bounce from the bottom. It additionally measures the depth of that reflection.
LIDAR makes use of oscillating mirrors to ship out laser pulses in lots of instructions in order to generate a “sheet” of sunshine because the drone strikes ahead. By means of measuring the timing and depth of the returning pulses, it will possibly present readings of the terrain and of factors on the bottom.
The sensor itself is just one a part of a LIDAR system. Critically necessary for capturing usable information, you’ll additionally want a high-precision satellite tv for pc positioning system (GNSS) in addition to high-accuracy sensors to find out the orientation of the LIDAR sensor in area—an inertial measurement unit (IMU). All of those high-end subsystems should work in good orchestration to allow processing of the uncooked information into usable data, a course of referred to as direct geo-referencing.
Because the sensors have developed, there’s now the choice to seize aerial LIDAR information from one in all two varieties of methods: classical manned airborne and light-weight UAV.
Classical airborne LIDAR surveys are performed from a crewed airplane and are much less correct however able to protecting extra floor than light-weight UAV LIDAR operations. Particularly, you may cowl between 10 and 1,000 sq. kilometers (4 and 400 sq. miles) in a single flight. Absolutely the accuracy will depend on the flight peak and sensor alternative. At a typical flight peak of two,000 meters (6,600 toes) above floor degree (AGL), you may count on an absolute accuracy restrict of about 20 cm (8 inches) horizontal and 10 cm (4 inches) vertical.
Light-weight drone LIDAR methods cowl as a lot because the drone permits per flight. As we are going to talk about intimately in under sections, these methods might be extra correct than these carried by manned plane. Particularly, fixed-wing drones carrying a LIDAR payload can cowl as much as 10 sq. km (4 sq. miles) in a flight, with absolute accuracy limits proper round 10 cm (4 inches) horizontal and 5 cm (2 inches) vertical.
In each circumstances of crewed plane and light-weight drone LIDAR, the accuracy is considerably lower than photogrammetry avails. Plus the post-processing for LIDAR completely requires experience past a fast coaching or studying of a handbook, as we’ll talk about under.
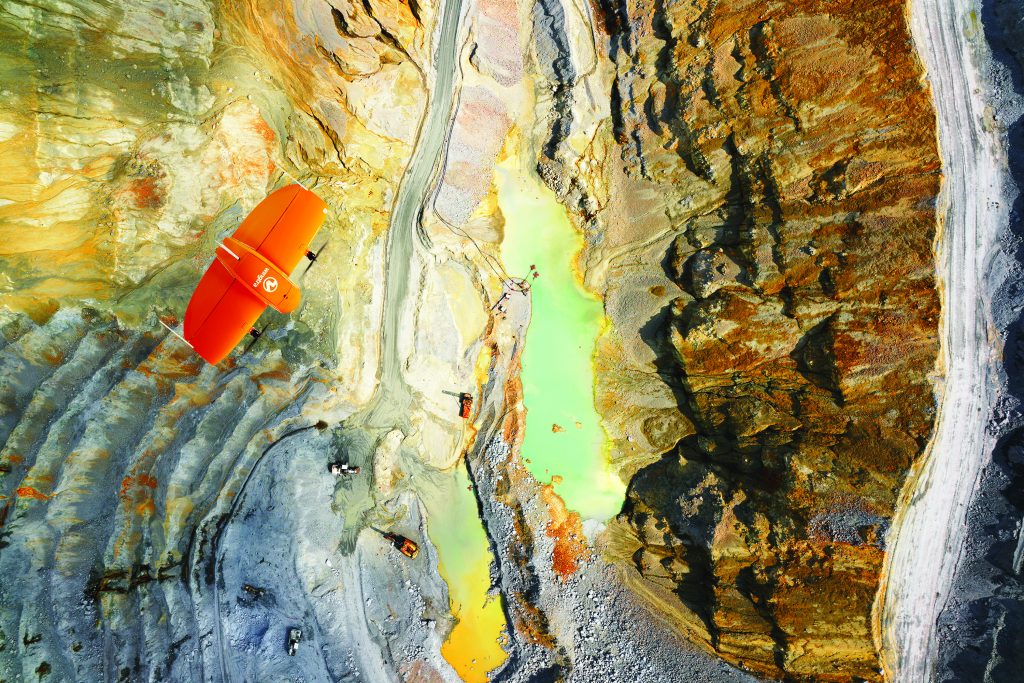

A WingtraOne UAV outfitted with a LIDAR sensor can create correct 3D fashions with 2 to three cm (0.8 to 1.2 in) of vertical accuracy. These fashions can be utilized for exact volumetric calculations throughout a variety of industries.
ACCURACY CONSIDERATIONS
As we have now seen, photogrammetry and aerial LIDAR differ in the way in which factors on the bottom are registered. This immediately impacts the ultimate level cloud accuracy and we are going to see that, particularly for horizontal accuracy of areas free from dense forest cover, photogrammetry clearly outperforms aerial LIDAR.
Photogrammetry. Within the case of photogrammetry, a top quality, high-resolution, full-frame sensor digicam like WingtraOne’s Sony RX1R II can yield outputs with horizontal (x-y) accuracies within the vary of 1 cm (0.4 in) and elevation (z) accuracies within the vary of two to three cm (0.8 to 1.2 inches) over onerous surfaces, enabling exact volumetric evaluation.
Notice, nevertheless, that to be able to obtain such efficiency the payload used for photogrammetry have to be knowledgeable one, with the appropriate picture sensor and lens to seize extra element. It’s not simply concerning the variety of pixels. In reality, two cameras with the identical variety of megapixels and completely different dimension sensors present completely different picture high quality and accuracy.
Correct mission planning and post-processing are additionally necessary for attaining optimum accuracy: good overlap amongst photographs will increase accuracy and supplies higher error correction in comparison with full reliance on the direct geo-referencing methodology utilized in LIDAR. A high-end drone system with skilled mission planning and post-processing workflow helps be sure that you seize high quality information that generates correct outcomes.
LIDAR. As for aerial LIDAR strategies, the sensor doesn’t goal particular options on floor however as an alternative shoots the beams at a set frequency in an outlined sample. Even when the horizontal accuracy of the one level may be greater, the very best horizontal accuracy of a focal point on the bottom is restricted by the purpose density.
Crewed aerial LIDAR can present a degree density of as much as 50 factors per sq. meter and presents a typical absolute accuracy of 20 cm horizontal and 10 cm vertical if flown at a typical peak of two,000 meters (6,600 toes) AGL.
By flying decrease, light-weight UAV LIDAR supplies the next level density than crewed aerial LIDAR and may obtain higher accuracy despite the fact that the laser is much less highly effective. Mounted on a multicopter, level density and the ensuing level cloud accuracy might be improved by flying low and sluggish on the expense of decreased effectivity.
Within the case of LIDAR on fixed-wing drones, a degree density between 50 and 200 factors per sq. meter is feasible. This implies a measurement each ~ 10 cm, so an absolute horizontal accuracy of about 10 cm might be achieved.
On high of restricted horizontal accuracy, LIDAR-derived level cloud accuracy will depend on the precision of the LIDAR itself and the standard of the INS (IMU and GNSS) system. Contemplating all technological developments and system variables presently, the standard absolute accuracy that you may count on from a light-weight LIDAR system on a fixed-wing drone is roughly 10 cm (4 inches) horizontal and 5 cm (2 inches) vertical.
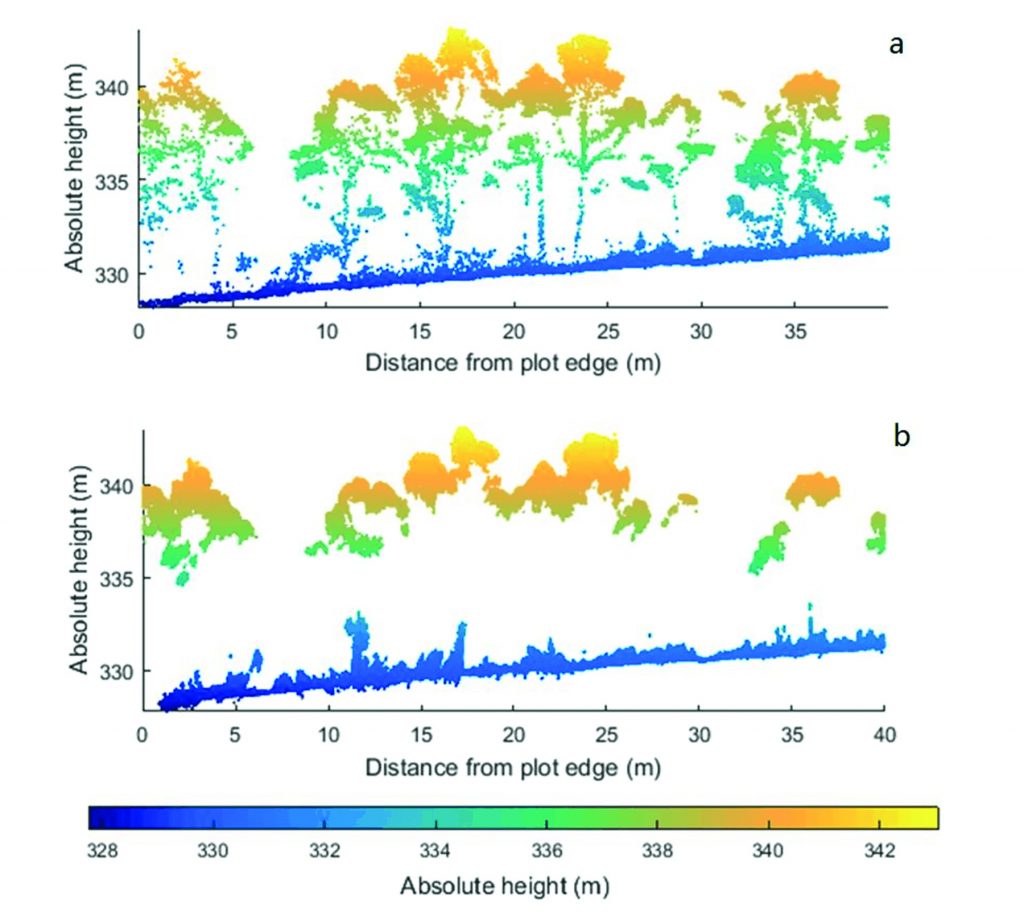
Whereas LIDAR can present extra element beneath denser vegetation, each photogrammetry (decrease graph) and LIDAR (high graph) can generate terrain fashions beneath sparse vegetation the place the bottom is partially seen from the air. (The info proven on this graphic was captured at 30 meters above the bottom.)
Photogrammetry and LIDAR Functions
For many missions, 3D outcomes achievable with photogrammetry are much like these obtained with LIDAR, however with higher accuracy and larger versatility, e.g., photorealistic outputs, due to the high-resolution visible information. There are some functions—particularly that includes energy strains or massive areas of dense forest cover—the place the upper expense of LIDAR for airborne missions is justified. Let’s have a look at the proof for this throughout a spread of precise functions.
Topographical maps that includes mild vegetation (sparse tree stands or open cover) are finest surveyed with high-resolution RGB information seize. The decision and photorealistic outcomes are helpful in circumstances like wildfire administration in residential areas and have been utilized by among the world’s largest city fireplace and rescue companies for the reason that data serves many stakeholders who want an actual view of what’s occurred.
Topographical maps with medium vegetation might be obtained by way of a mix of photogrammetry and a way to seize the bottom under the vegetation. To seize the extra data under the vegetation, floor survey strategies or aerial LIDAR can be utilized. The mix with floor survey strategies retains the worth down whereas guaranteeing excessive accuracy plus the decision and photorealistic outcomes obtainable by way of photogrammetry.
Whereas LIDAR can present extra element beneath denser vegetation, each photogrammetry and LIDAR can generate terrain fashions beneath sparse vegetation the place the bottom is partially seen from the air.
Giant-scale topographical maps that includes heavy vegetation are finest acquired by way of manned airborne LIDAR. A digital terrain mannequin (DTM) of the forest floor supplies helpful data for venture planning in development (e.g., the planning of recent roads), forest biomass or detailed data on vegetation and habitats by way of topography and underlying terrain, functions falling underneath these circumstances will at all times require LIDAR at the very least partly to normalize topographical information.
Usually, state companies attempt to preserve fairly correct digital terrain fashions (DTMs) of the forest grounds. For these sorts of large-scale tasks with low decision necessities, manned airborne LIDAR is probably the most cost-effective possibility obtainable. If a extra correct or up-to-date DTM of a small forest is required, a standard floor survey would be the most cost-effective possibility obtainable, but light-weight drone LIDAR would possibly fill a distinct segment in-between.
Naked-earth mining, volumetric and pure useful resource surveys are finest dealt with by high-end RGB payloads. Even huge surveys are very best with the appropriate drone and RGB digicam. On high of this, photogrammetry is value efficient and saves time not solely to seize and course of information associated to chop and fill volumes, stockpile assessments and standing stories, but in addition to share this data and reconcile with contractors and stakeholders.
Energy line surveys for vegetation management might be executed with LIDAR or high-resolution photogrammetry and powerline extraction options on software program like Pix4Dsurvey. For the sake of photorealism, value, and workflow, I like to recommend the latter possibility. Analysis is ongoing round photogrammetry as a go-to, cost-effective resolution.
Powerline pole tower inspection advantages from dwell video inspection with a multicopter carrying an RGB or thermal payload. These are often comparatively small areas that multicopters can maneuver round and take indirect pictures of simply and safely. With this methodology, you get all data inside a really quick period of time. Zoom cameras enable detailed inspection that can not be provided by photogrammetry or LIDAR..
Rail observe inspection continues to be most frequently carried out from the bottom—by a prepare outfitted with ultrasonic, LIDAR, and visible sensors. Inspection from the air with both photogrammetry or aerial LIDAR is gaining increasingly more curiosity however each strategies are in early levels. Excessive-resolution photogrammetry presents information that avails outputs with the entire important particulars precisely and autonomously whereas saving time. Plus the photorealism provides a component of straightforward identification and flexibility that may reply to a spread of questions.

Metropolis mapping with vertical constructions requiring 3D vantage factors has been extensively demonstrated with photogrammetry based mostly on imagery captured with a payload that includes indirect capabilities. For cityscapes with many high-rises and intense ranges of vertical element, multicopters work effectively, though their capability to cowl wide-spread areas per flight is compromised. VTOL drones carrying indirect payloads can nonetheless seize huge areas and obtain spectacular vertical accuracy.
Operational concerns
The distinction between photogrammetry and LIDAR grows when contemplating operational and logistical components. To generate high quality outcomes, a LIDAR system requires all of its parts to work completely in sync. Small gaps or errors in sensor measurements can result in vital errors in outputs. Or worse, outputs that “look” proper however should not. Methods like floor management factors (GCPs), that are helpful in photogrammetry to right points, are tougher to implement with LIDAR. More often than not, the one resolution for inaccurate LIDAR information is to repeat flights.
LIDAR tasks require an professional who understands the workflow and particulars of every subsystem and may acknowledge constant and correct information.
In distinction, photogrammetry-based workflows are extra forgiving. The redundancy created by a number of, overlapping photographs of the identical level on the bottom permits error correction throughout processing and interprets to high-accuracy outputs, even in non-ideal circumstances or operations. The shorter studying curve for drone-based photogrammetry (even for operators with no prior expertise), results in larger flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
The convenience of use of photogrammetry options just like the WingtraOne interprets into larger operational flexibility, the flexibility to deploy a number of methods to cowl distributed websites, larger frequency of captures, and general decreased prices.
Photogrammetry permits the creation of correct 3D maps of huge areas. Photogrammetry outputs additionally embrace high-resolution visible information in full shade for each level on the map to assist within the interpretation.
Last ideas
We now have explored the variations between how photogrammetry and LIDAR work and the similarities of their outputs and realized about conditions the place every expertise might be finest utilized. And whereas some particular functions would possibly justify the associated fee and complexity of LIDAR, photogrammetry can meet a lot of the on a regular basis challenges introduced throughout a spread of tasks and industries, offering distinctive accuracy and stunningly detailed maps, obtainable on demand and with minimal experience overhead.
So should you don’t want what LIDAR uniquely supplies—particularly to mid- or large-scale forests with heavy however penetrable cover—you are able to do extra utilizing photogrammetry coupled with knowledgeable drone for considerably much less cash and complexity.

